what is an organelle how are organelles related to cells
Firstly, what is an organelle? Organelles are small subcellular structures located in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, and in more complex eukaryotic cells, organelles are often enclosed by their own membrane. Each organelle performs a specialised function for that prison cell, much like an organ does for the body.
Across the use of organelle-specific protein markers, nosotros can besides employ organelle-selective dyes to highlight structures of interest thus aiding your enquiry into each of these specialist structures. Below we summarize how to go the most out of staining when identifying private jail cell organelles (Figure 1).
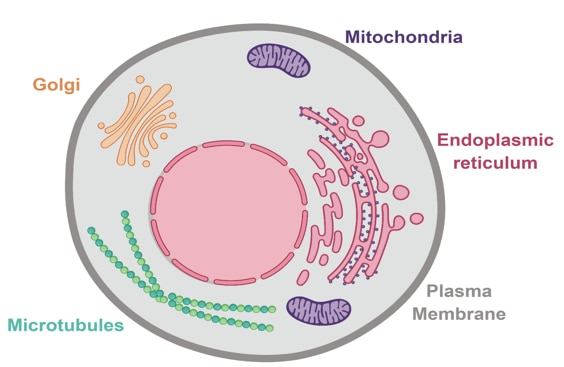
Figure 1. Brute cell highlighting some of the key organelles that tin can be stained with organelle-specific dyes.
Four considerations before selecting a dye:
Before we discuss the unlike dyes available for the different organelles, we must showtime consider sure points in order to ensure we get the best results from our stains.
1. Consider the membrane permeability of the dye.
DAPI has a low membrane permeability and is suitable for staining fixed cells. Hoechst (e.k., 33342) has a college membrane permeability and tin too be used in alive cells.
2. Think about your fluorescent wavelengths.
For example, if you were identifying a poly peptide of interest at the lipid membrane using a secondary antibody emitting light in the green aqueduct, it is better to cull a lipid dye that emits lite in the far-red aqueduct. That mode, you tin avoid them interfering with each other.
iii. Determining the concentration of your dye is crucial
As well depression a concentration will not provide a strong visualization, while likewise high a concentration will be toxic to your samples.
4. Sympathize exactly how the dye works
Mitochondrial dyes like Rhodamine are dependent on membrane potential. They can only be applied to live cells, making them useful tools to clarify health and cell viability. Lysosome dyes require the acidic environment of this organelle to work properly. They as well piece of work best in alive cells.
Different dyes for different organelles
1. Plasma membranes and the Golgi complex
The entire jail cell is enclosed by a phospholipid bilayer, the plasma membrane, and contains several membrane networks within the cytoplasm. The selective permeability of the plasma membrane and the formation of vesicles are essential for controlling the internal environment and the transport of proteins within the cell.
Importantly, please consider the membrane permeability of the dye. Membranes tin can be stained with lectins, which are saccharide-binding proteins that recognize and bind to certain parts of sugars.
Lectins such as wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) will stain the plasma membrane but besides the Golgi, an organelle composed of many membrane sacs and vesicles involved in intracellular poly peptide processing. Both structures are formed from the phospholipid bilayer, and both tin be stained using lectins.
Please note: Some lectins are specific to particular glycolipids and glycoproteins. This is extremely useful when imaging multiple cell types. For example, lectin IsoB4 specifically stains endothelial cells past binding to their basal membrane.
2. ER and lipid droplets
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is another membrane organization, continuous with the nuclear membrane and involved in the processing of lipids and proteins. The tubular cisternae and flattened sheets of the ER tin can make up nigh 10% of the entire jail cell volume. Information technology tin exist classified into rough ER (associated with ribosomes and involved in poly peptide production) or smooth ER (not associated with ribosomes and involved in lipid metabolism). Dyes such as Nile Red bind to lipid droplets and stain all lipophilic membranes, forth with any intracellular lipid aerosol. However, dyes such as this can show a lot of background staining, so optimize carefully to ensure reliable results.
Please note: Treating cells with oleic acid before staining with lipid-specific dyes will induce lipid droplet formation. This tin be used as a positive control to bank check if the stain is working as expected.
3. Lysosomes
Lysosomes are described equally the digestive organization of the cell; they contain degradative enzymes. To maintain the function of these enzymes, the lysosome must remain in acidic conditions (around pH 5), in contrast to the neutral pH of the cytoplasm, meaning they require the active transport of protons from the cytoplasm. Information technology is best to use a cell-permeable dye that specifically works in acidic environments and accumulates via the pH gradient into the lysosome.
Please note: Lysosome dyes such as Neutral Reddish require an acidic surroundings for this organelle and work all-time in alive cells. One tip, is to commencement add the lysosome dye before later fixing your cells, thus enabling the add-on of protein-specific antibodies afterwards.
iv. Mitochondria
Mitochondria are considered to be the powerhouse of the prison cell. They produce almost 90% of the energy required for survival by the oxidative phosphorylation process, and are besides a key thespian in apoptosis. They accept two membranes that utilise a proton gradient to generate ATP, using information technology as intermediate energy storage. This membrane potential enables the use of mitochondrial dyes such every bit Rhodamine, a useful tool to clarify cell wellness and viability in alive cells. However, it can only exist applied right before fixation as the membrane potential is degraded.
Please note : Rhodamine is toxic and inhibits mitochondrial part.
5. Microtubules
Microtubules are one of the structural components of the cell that grade the cytoskeleton, along with actin and intermediate filaments. While not strictly organelles, microtubules are of import in understanding the fundamental processes governing cells and can likewise help when visualizing a whole cell. They tin exist identified using tubulin dyes, which, depending on the specific bounden affinity, may touch on the microtubule dynamics and could halt mitosis.
Please note: Use methanol fixation rather than paraformaldehyde. This will avoid interference with cross-linking proteins and will produce better-quality images.
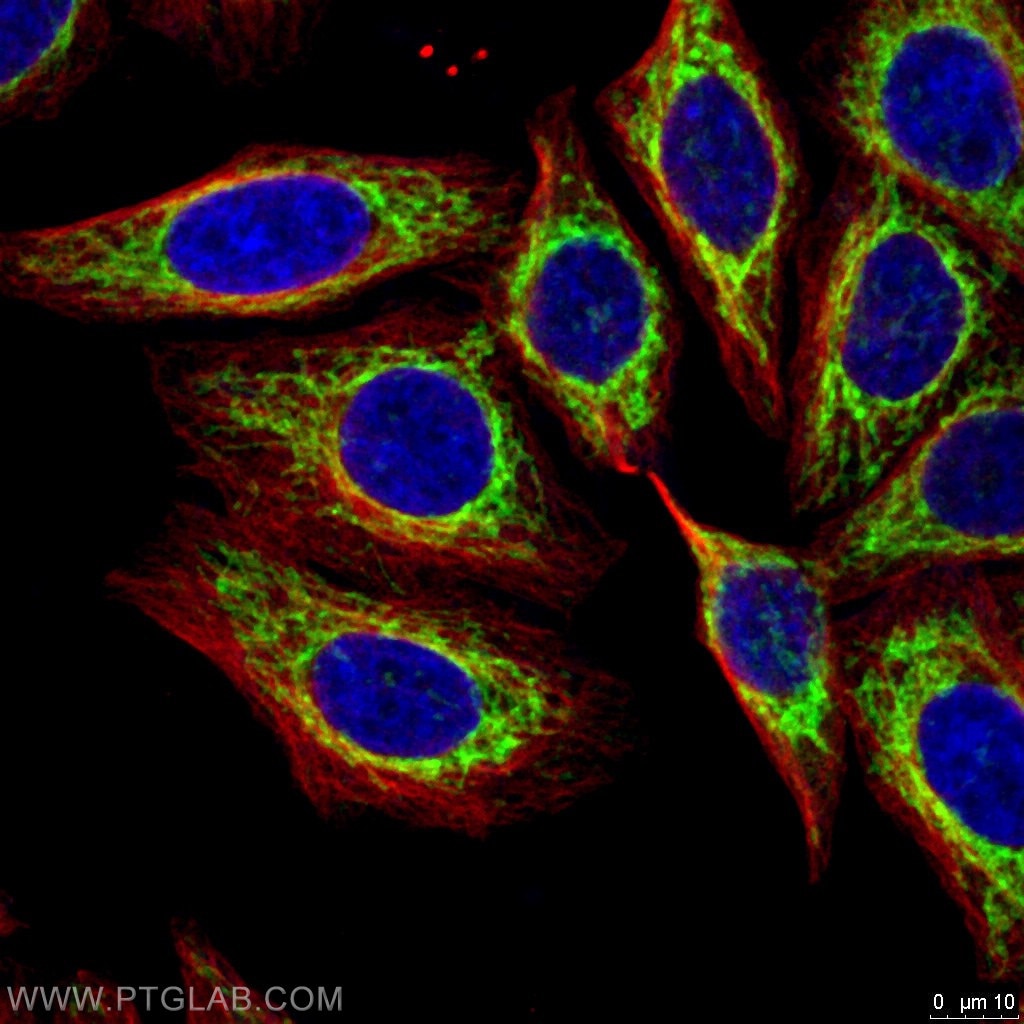
Figure 2. Immunofluorescent assay of iv% PFA fixed HepG2 cells using FIS1 andAlpha Tubulin antibodies.Green: FIS1 (10956-1-AP); Red: Alpha Tubulin (66031-1-Ig)
Please remember to trust your dye!
Using dyes is a simple and constructive way to visualize organelles in your research, alongside antibody staining. Ensure you thoroughly enquiry the different options available to you, thus ensuring the best chances for success!
For more information on general staining tips, and multiple immunostaining technique bank check out technical tips on optimizing IF experiments.
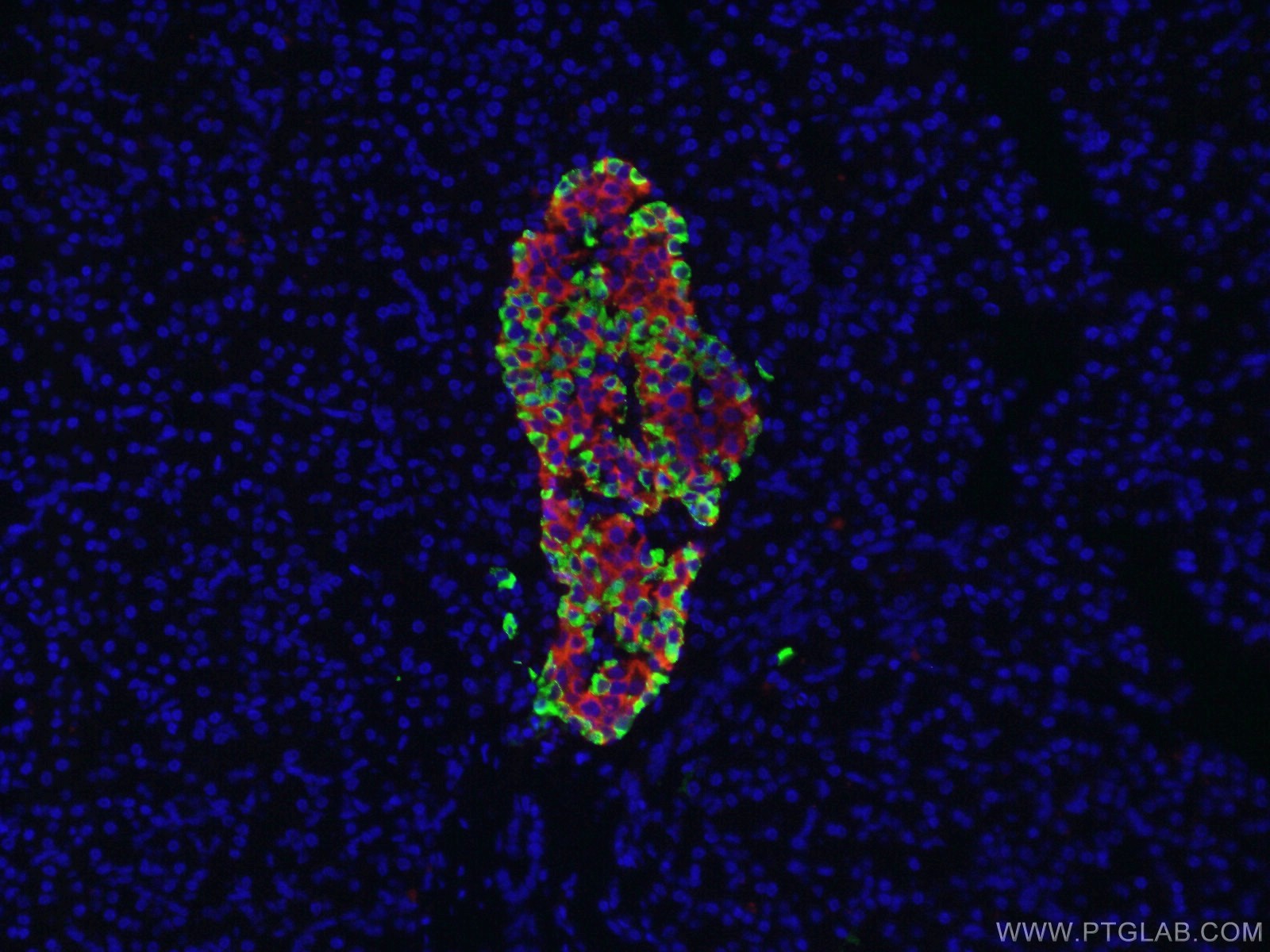
Effigy 3. Immunofluorescent assay of 4% PFA fixed human pancreas tissue using Glucagon andInsulin antibodies. Green: Glucagon (15954-1-AP); Red: Insulin (66198-one-Ig)
Source: https://www.ptglab.com/news/blog/dying-to-see-what-s-inside-staining-organelles/
0 Response to "what is an organelle how are organelles related to cells"
Post a Comment